Respiratory Support
Respiratory support (mechanical ventilation) is a method to mechanically assist or replace spontaneous breathing in patients suffering from Respiratory Distress Symptom (RDS). Respiratory Distress Symptom is an acute disorder (ARDS) characterized by inflammation of the lung parenchyma leading to impaired gas exchange, i.e. failure of the respiratory (lung) system to provide enough oxygen to the body (O2) and/or failure of the lungs to remove the carbon dioxide (CO2) from the blood. Respiratory failure requires immediate medical attention and is the major indicator for the use of mechanical ventilation.
Mechanical ventilation is the use of a breathing machine (e.g. respirator, ventilator, inhalator) to assist or replace spontaneous breathing in patients. Mechanical ventilation is divided into two categories :
a. invasive ventilation (INV), when the patient is connected to the ventilator through a tube (called an endotracheal tube), that is placed in the windpipe
b. non-invasive ventilation (NIV), refers to the administration of ventilatory support without using an invasive artificial airway (endotracheal tube or tracheostomy tube). It is applied by a non-invasive continuous positive airway pressure ventilatory assist machine (BiPAP) through a mask.
Articles sources: 01. anesthesia.gr 02. Magazine PNEUMON, Volume 16
Respiratory Support Products :
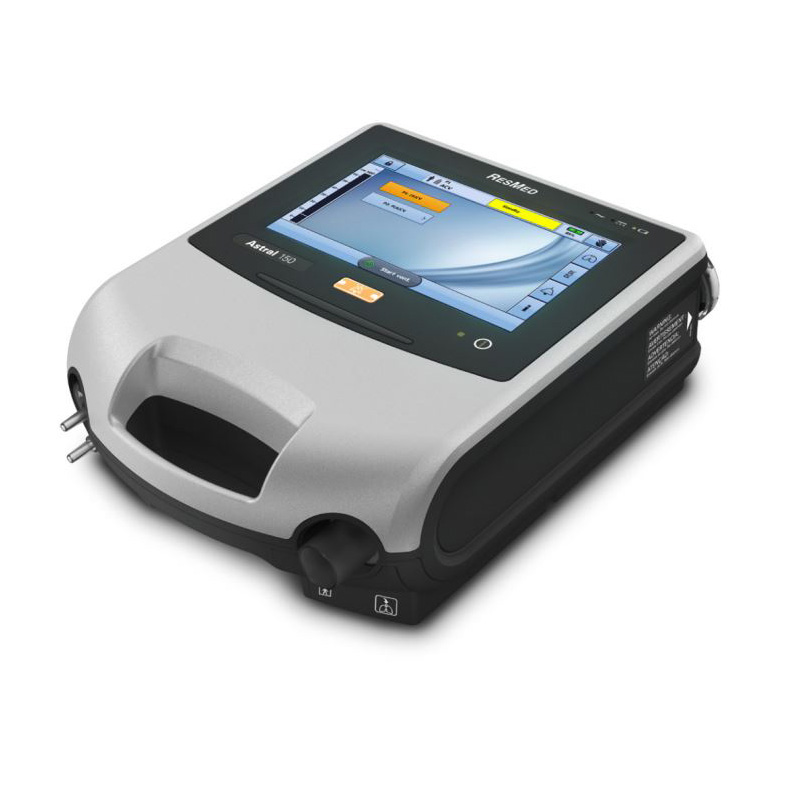

Pressure – Volume Ventilator Astral 100
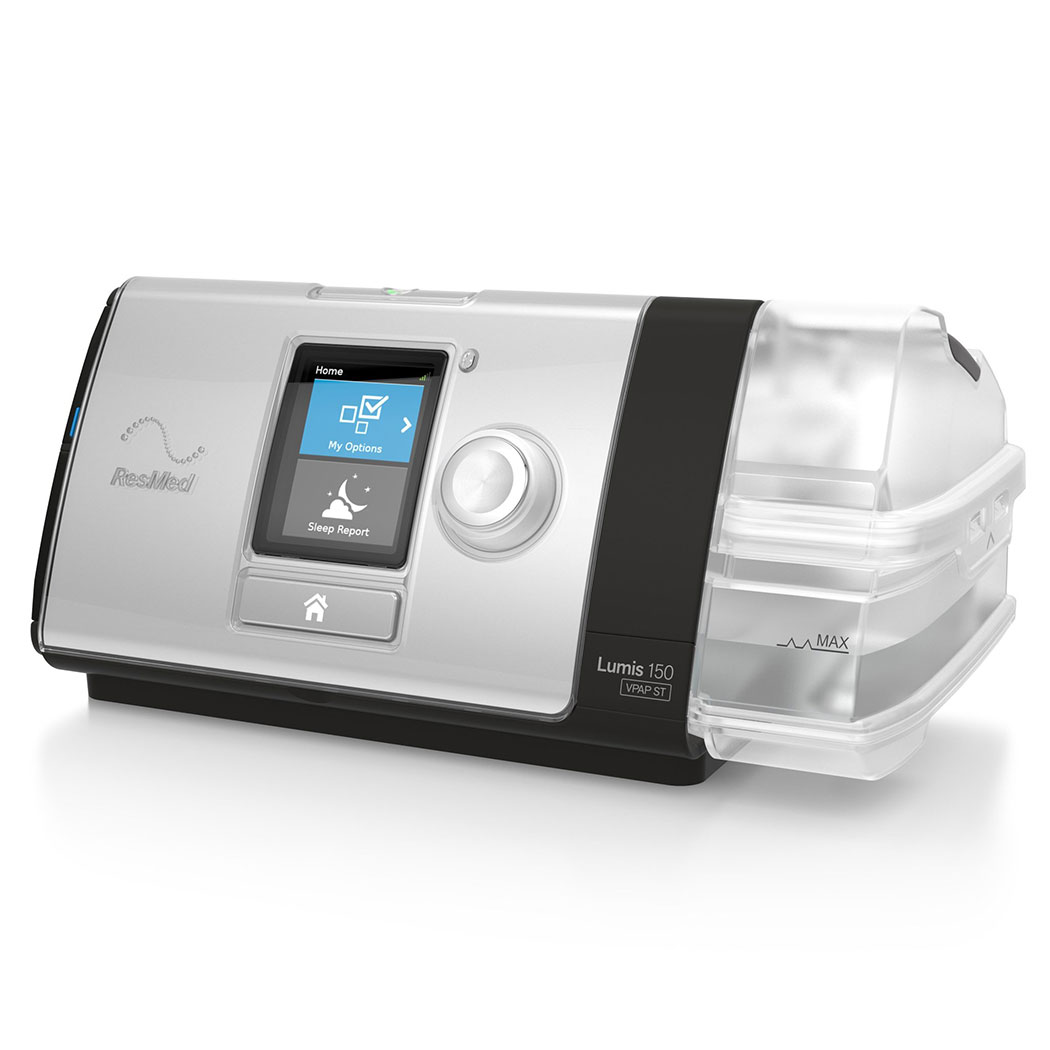
Bi-Pap ST Lumis 150
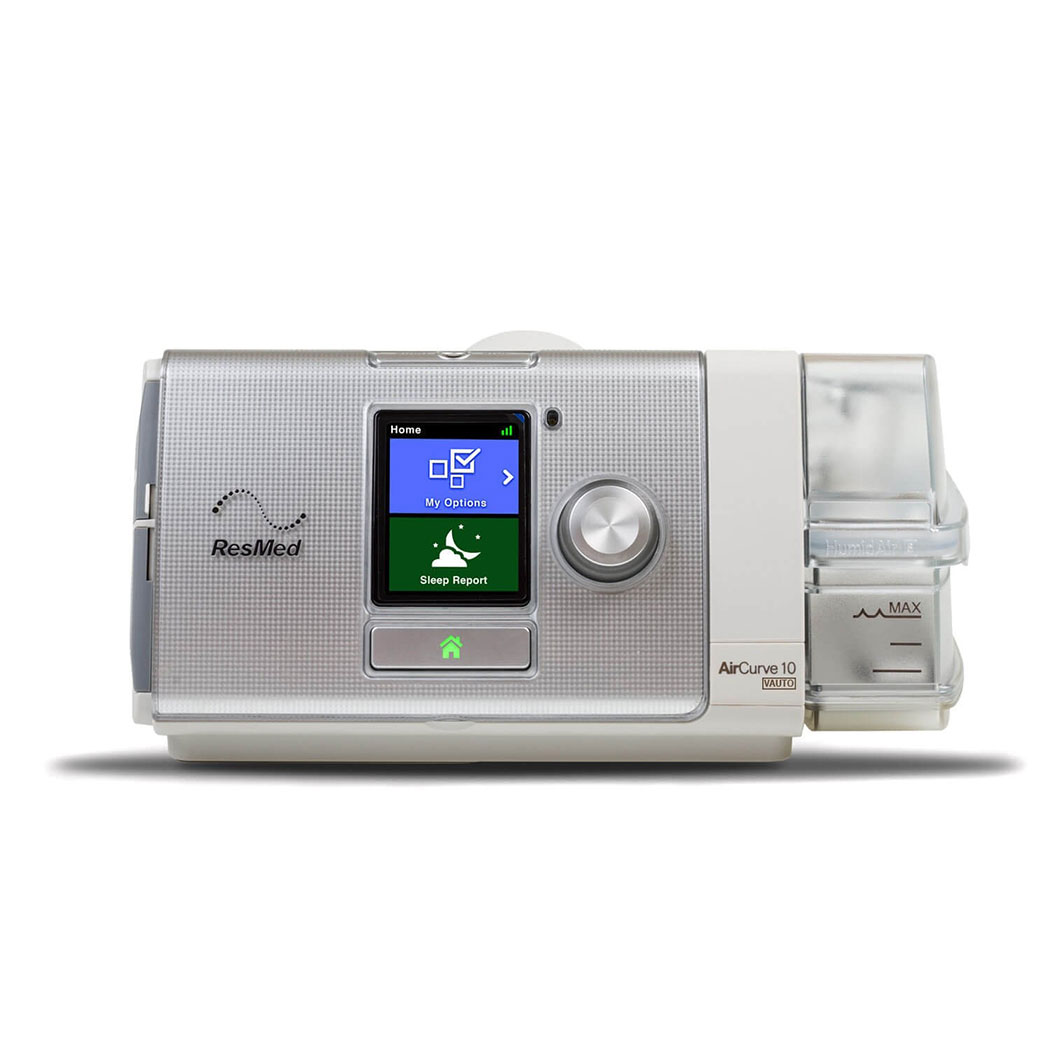

Bi-Pap S AirCurve10S
area of activity
RESPIRATORY SUPPORT PRODUCTS
GEOGRAPHICAL COVERAGE

Western Greece





